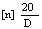S.I. No. 35/1980 -- Health (Emulsifiers, Stabilisers, Thickening and Gelling Agents in Food) Regulations, 1980.
1980
35
|
|
S.I. No. 35/1980:
HEALTH (EMULSIFIERS, STABILISERS, THICKENING AND GELLING AGENTS IN FOOD) REGULATIONS, 1980.
|
|
|
HEALTH (EMULSIFIERS, STABILISERS, THICKENING AND GELLING AGENTS IN FOOD) REGULATIONS, 1980.
|
|
|
The Minister for Health, in exercise of the powers conferred on him by sections 5 , 54 and 59 of the Health Act, 1947 (No. 28 of 1947), subsection (3) of section 38 of the Health Act, 1953 (No. 26 of 1953) and section 6 of the Health Act, 1970 (No. 1 of 1970), after consultation with the Minister for Industry, Commerce and Energy and the Minister for Agriculture, hereby makes the following Regulations:--
|
|
|
PART I. Preliminary and General.
|
|
|
1. These Regulations may be cited as the Health (Emulsifiers, Stabilisers, Thickening and Gelling Agents in Food) Regulations, 1980.
|
|
|
2. These Regulations shall come into effect on the 1st day of March, 1980.
|
|
|
3. (1) In these Regulations, unless the context otherwise requires--
|
|
|
"the Act" means the Health Act, 1947 ;
|
|
|
"appropriate description" means, as respects any permitted emulsifier or permitted stabiliser, a name or description, or a name or description sufficiently specific in each case, to indicate to an intending purchaser the true nature of the permitted emulsifier or permitted stabiliser to which it is applied;
|
|
|
"authorised officer" means an authorised officer for the purposes of Part II of the Act;
|
|
|
"bread" includes the following and any part of the following--baps, breadrolls, fancy bread, milk bread, malt bread and fruit bread;
|
|
|
"cheese spread" means cheese which has been melted and mixed with milk products other than cheese with or without the addition of emulsifying salts;
|
|
|
"processed cheese" means cheese which has been subjected to a process of melting and mixing with or without the addition of emulsifying salts;
|
|
|
"soft cheese" means cheese which is readily deformed by moderate pressure but does not include whey cheese, processed cheese or cheese spread and any reference to soft cheese includes a reference to cream cheese or curd cheese;
|
|
|
"whey cheese" means the product obtained by (i) concentrating whey with or without the addition of milk and milk fat and moulding such concentrated whey, or (ii) coagulating whey with or without the addition of milk and milk fat;
|
|
|
"container" includes any form of packaging of food and any wrapper or band;
|
|
|
"cream" means that portion of milk rich in milk-fat which has been separated by skimming or otherwise;
|
|
|
"emulsifier, stabiliser, thickening and gelling agent" mean, respectively, any substance which, when added to a food, is capable--
|
|
|
( a ) in the case of an emulsifier, of aiding the formation of, and in the case of a stabiliser, of maintaining a uniform dispersion of, two or more immiscible substances;
|
|
|
( b ) in the case of a thickening agent, of increasing its viscosity; and
|
|
|
( c ) in the case of a gelling agent, of giving it the consistency of a gel;
|
|
|
but do not in any case include:--
|
|
|
(i) any natural food substance;
|
|
|
(ii) products containing pectin and derived from dried apple pomace or dried peel of citrus fruits, or from a mixture of both, by the action of dilute acid followed by partial neutralisation with sodium or potassium salts;
|
|
|
(iii) caseins and caseinates;
|
|
|
(iv) proteins, protein concentrates and protein hydrolysates;
|
|
|
(v) starches, whether modified or not;
|
|
|
(vi) normal straight chain fatty acids derived from food fats;
|
|
|
(vii) acids, bases and salts which, when added to a food during the process of manufacture, change or stabilise the pH;
|
|
|
(viii) any substance, the use of which is permitted under Regulations, other than these Regulations, for the time being in force under Part V of the Act, with the exception of lecithin, potassium orthophosphates, sodium orthophosphates, calcium orthophosphates, potassium pyrophosphate, sodium pyrophosphate, sodium acid salt of pyrophosphoric acid and sodium tripolyphosphate.
|
|
|
"food" has the meaning assigned to it in Part V of the Act;
|
|
|
"Food Chemicals Codex 1972", "First Supplement, 1974" and "Second Supplement, 1975" mean, respectively, the second edition of the Food Chemicals Codex published in 1972, the First Supplement to that edition published in 1974 and the Second Supplement to that edition published in 1975, in each case, by the National Academy of Sciences, Washington D.C., United States of America;
|
|
|
"natural food substance" means any substance, suitable for use as food and commonly used as food, which is wholly a natural product, whether or not that substance has been subjected to any process or treatment, and includes malt extract and glucose syrup but does not include edible gums;
|
|
|
"permitted emulsifier" and "permitted stabiliser" mean, respectively, any emulsifier and any stabiliser in Part I of Schedule 1 which complies with the specific purity criteria in relation to that emulsifier or stabiliser referred to in Part II of that Schedule and, so far as is not otherwise provided in any such specific purity criteria, with the general purity criteria in Part III of that Schedule, and includes any mixture of two or more such emulsifiers or stabilisers or emulsifiers and stabilisers;
|
|
|
"sell" includes supply, offer or expose for sale or have in possession for sale and cognate words shall be construed accordingly;
|
|
|
"specified food" means any food of a description specified in Column 1 of Part I or Part II of Schedule 2.
|
|
|
(2) Any reference in these Regulations to an emulsifier or stabiliser shall be construed as including a reference to a thickening agent or gelling agent.
|
|
|
(3) Unless a contrary intention is expressed, all proportions mentioned in these Regulations are proportions calculated by weight of the product as manufactured, prepared, imported, distributed or sold.
|
|
|
(4) Any reference to a label borne on a container shall be construed as including a reference to any legible marking on the container.
|
|
|
(5) For the purposes of these Regulations, the supply of food, otherwise than by sale, at, in or from any place where food is supplied in the course of a business, shall be deemed to be a sale of that food.
|
|
|
(6) Any reference in these Regulations to an owner or to a person responsible for food shall, in the case of food purchased from a vending machine, be construed as a reference--
|
|
|
( a ) where the name and address of the proprietor is stated on the machine and such address is in the State, to the proprietor of the machine;
|
|
|
( b ) in other cases, to the occupier of the premises at or on which the machine stands or to which it is affixed.
|
|
|
(7) Any reference in these Regulations to any other Regulations shall be construed as a reference to such Regulations as amended by subsequent Regulations.
|
|
|
(8) Any reference in these Regulations to a numbered article or schedule shall, unless the reference is to an article or schedule of specified Regulations, be construed as a reference to the articles or schedules bearing that number in these Regulations.
|
|
|
4. These Regulations shall be enforced and executed by health boards in their functional areas.
|
|
|
5. (1) Where a sample of any food has been certified under the Health (Sampling of Food) Regulations, 1970 ( S.I. No. 50 of 1970 ) not to comply with these Regulations, an authorised officer may seize, remove and detain such food as being food which is unfit for human consumption.
|
|
|
(2) With the consent in writing of the owner or person responsible for such food, an authorised officer may destroy or otherwise dispose of it so as to prevent its use for human consumption.
|
|
|
(3) An authorised officer who has seized any food in pursuance of this article may, on giving notice in writing to the owner or person responsible for such food of his intention to do so, apply to a Justice of the District Court for an order directing that such food be destroyed or otherwise disposed of as being food which is unfit for human consumption.
|
|
|
(4) A Justice of the District Court to whom the application is made for an order under sub-article (3) of this article shall, if satisfied that such food does not comply with these Regulations, order that it be destroyed or otherwise disposed of after such period, not exceeding fourteen days, as may be specified in such order, as being food which is unfit for human consumption and an authorised officer shall destroy or dispose of it accordingly.
|
|
|
6. A person shall give to any authorised officer all reasonable assistance that the officer may require in the performance of his duties under these Regulations and such assistance shall include the giving of information in relation to the composition and use of any food and the identity of the person from whom or the place from which any such food has been obtained and the person to whom and the place to which it has been consigned or the manner in which it has otherwise been disposed of.
|
|
|
7. These Regulations shall not apply to foods for export or re-export.
|
|
|
PART II. Sale, Distribution and Importation of Food containing Emulsifiers and Stabilisers.
|
|
|
8. (1) Subject to the provisions of these Regulations no food which is manufactured, prepared, imported, distributed or sold shall contain any added emulsifier or added stabiliser other than a permitted emulsifier or a permitted stabiliser.
|
|
|
(2) Subject to sub-article (4) of this article any specified food described in Column 1 of Part I of Schedule 2, but no other food, which is manufactured, prepared, imported, distributed or sold, may contain any permitted emulsifier or permitted stabiliser of the description and in the proportion specified in relation thereto in Column 2 and Column 3, respectively, of that Part of that Schedule.
|
|
|
(3) Subject to sub-article (5) of this article any specified food described in Column 1 of Part II of Schedule 2 which is manufactured, prepared, imported, distributed or sold may, subject to the provisions of the footnote to that Part, contain any permitted emulsifier or permitted stabiliser of the description and in the proportion specified in relation thereto in Column 2 and Column 3, respectively, of that Part of that Schedule, and any such specified food shall contain no other permitted emulsifier or permitted stabiliser.
|
|
|
(4) ( a ) Nothing in sub-articles (2) and (3) of this article shall prohibit the presence in or on any food, which contains any specified food as an ingredient, of any permitted emulsifier or permitted stabiliser of the description specified for, and in the amount appropriate to, the quantity of that specified food in accordance with the said sub-articles.
|
|
|
( b ) Notwithstanding the provisions of paragraph (a) of this sub-article, where, by reason of the use of a tin-greasing emulsion in its preparation, any food contains--
|
|
|
(i) the permitted emulsifier oxidatively polymerised soya bean oil, that permitted emulsifier shall be present in a proportion not exceeding 50 milligrams per kilogram;
|
|
|
(ii) the permitted emulsifier polyglycerol esters of dimerised fatty acids of soya bean oil, that permitted emulsifier shall be present in a proportion not exceeding 20 milligrams per kilogram.
|
|
|
(5) Nothing in sub-article (3) of this article shall prohibit the presence in or on any bread, by reason of the use of a tin-greasing emulsion in its preparation, of any permitted emulsifier or permitted stabiliser not specified in the proviso to the preceding sub-article or in Column 2 of item (a) of Part II of Schedule 2 in a proportion not exceeding 50 milligrams per kilogram.
|
|
|
(6) No flour, intended for sale for human consumption, shall contain any emulsifier or stabiliser.
|
|
|
(7) Subject to the exception made in Part II of Schedule 2 for whipping cream or whipped cream which is sold, consigned or delivered to a manufacturer for the purposes of his manufacturing business, or to a caterer for the purposes of his catering business, no cream when sold as such shall contain an emulsifier or stabiliser.
|
|
|
(8) The emulsifiers listed in Part I, Schedule 1 of these Regulations under serial numbers E407 and E440 may contain one or more of the sugars as defined in the Food Standards (Certain Sugars) (European Communities) Regulations 1975 ( S.I. No. 118 of 1975 ).
|
|
|
(9) A person shall not manufacture, prepare, import, distribute or sell any food which does not comply with these Regulations.
|
|
|
PART III. Sale, Advertisement and Labelling of Emulsifiers and Stabilisers.
|
|
|
9. (1) The package or container in which any permitted emulsifier or permitted stabiliser, either alone or in combination with any other substance, is imported, distributed or sold for use as an ingredient in the manufacture or preparation of food, shall bear a label containing the information specified in Schedule 3.
|
|
|
(2) A person shall not sell any permitted emulsifier or permitted stabiliser which does not comply with these Regulations.
|
|
|
(3) A person shall not publish any advertisment of any permitted emulsifier or permitted stabiliser for sale for use as an ingredient in the preparation of food, which bears or includes any words, device or description calculated to indicate either directly or indirectly that that emulsifier or stabiliser is a nutritive substitute for fat or eggs.
|
|
|
PART IV. Amendments and Revocations.
|
|
|
10. The Health (Arsenic and Lead in Food) Regulations, 1972 ( S.I. No. 44 of 1972 ) shall be amended as follows:--
|
|
|
( a ) the items "Pectin (liquid)" and "Pectin (solid)" in Column 1 of Part I of the Schedule to the said Regulations, and the relevant numbers in Column 2 of the said Part, shall be deleted,
|
|
|
( b ) The items "Alginic acid, alginates, agar, carrageen and similar products derived from seaweed", "Lecithin", "Pectin (liquid)" and "Pectin (solid)" in Column 1 of Part II of the Schedule to the said Regulations, and the relevant numbers in Column 2 of the said Part, shall be deleted.
|
|
|
11. The Health (Antioxidant in Food) Regulations, 1973 ( S.I. No. 148 of 1973 ) shall be amended as follows:--
|
|
|
( a ) the deletion of the definition of "partial glycerol esters" in article 4 of the said Regulations,
|
|
|
( b ) the substitution in Column 1 of item (b) of Part I of the First Schedule for the words "Partial glycerol esters", of the words "Any permitted emulsifier or permitted stabiliser containing combined fatty acids whether or not these fatty acids have been polymerised".
|
|
|
12. The Public Health (Saorstat Eireann) (Preservatives, etc., in Food) Regulations, 1928 (S.R. & O. 1928 No. 54) are hereby revoked.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SCHEDULE 1.
|
|
|
PART I.
|
|
|
Permitted Emulsifiers and Permitted Stabilisers.
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Column 1 |
Column 2 |
| Name of Emulsifier or Stabiliser |
Serial Number |
| Lecithins |
E 322 |
| Ammonium phosphatides or Emulsifier YN |
-- |
| Sodium orthoposphates |
E 339 |
| Potassium orthophosphates |
E 340 |
| Calcium orthoposphates |
E 341 |
| Alginic acid |
E 400 |
| Sodium alginate |
E 401 |
| Potassium alginate |
E 402 |
| Ammonium alginate |
E 403 |
| Calcium alginate |
E 404 |
| Propane-1,2-diol alginate |
E 405 |
| Agar |
E 406 |
| Carrageenan |
E 407 |
| Locust bean gum |
E 410 |
| Guar gum |
E 412 |
| Tragacanth |
E 413 |
| Acacia or gum arabic |
E 414 |
|
(i) Sorbitol
|
E 420 |
|
(ii) Sorbitol syrup
|
E 420 |
| Mannitol |
E 421 |
| Glycerol |
E 422 |
| Pectin |
E 440 A |
| Amidated Pectin |
E 440 B |
| Ghatti-gum |
-- |
| Karaya gum or sterculia gum |
-- |
| Zanthan gum |
-- |
|
(i) diSodium dihydrogen diphosphate or sodium acid salt of pyrophosphoric acid.
|
E 450 (a) |
|
(ii) triSodium diphosphate or sodium pyrophosphate
|
|
|
(iii) tetraSodium diphosphate or tetraSodium pyrophosphate
|
|
|
(iv) tetraPotassium diphosphate or potassium pyrophosphate
|
|
|
(i) penta Sodium triphosphate or sodium tripolyphosphate
|
E 450 (b) |
|
(ii) pentaPotassium triphosphate
|
|
|
(i) sodium polyphosphate
|
E 450 (c) |
|
(ii) potassium polyphosphate
|
|
| Microcrystalline cellulose |
E 460 |
| Methylcellulose |
E 461 |
| Hydroxypropylcellulose |
E 463 |
| Hydroxypropylmethylcellulose |
E 464 |
| Ethylmethylcellulose |
E 465 |
| Carboxymethycellulose |
E 466 |
| Sodium, potassium and calcium salts of fatty acids |
E 470 |
| Mono-and di-glycerides of fatty acids |
E 471 |
| Acetic acid esters of mono-and diglycerides of fatty acids |
E 472 (a) |
| Lactic acid esters of mono-and di-glycerides of fatty acids |
E 472 (b) |
| Citric acid esters of mono-and di-glycerides of fatty acids |
E 472 (c) |
| Tartaric Acid esters of mono-and di-glycerides of fatty acids |
E 472 (d) |
| Mono-and diacetyltartaric acid esters of mono-and di-glycerides of fatty acids |
E 472 (e) |
| Mixed acetic/tartaric acid esters of mono-and diglycerides of food fatty acids |
E 472 (f ) |
| Sucrose esters of fatty acids |
E 473 |
| Sucroglycerides |
E 474 |
| Polyglycerol esters of fatty acids |
E 475 |
| Partial polyglycerol esters of polycondensed fatty acids of castor oil |
-- |
| Polyglycerol esters of dimerised fatty acids of soya bean oil |
-- |
| Oxidatively polymerised soya bean oil |
-- |
| Propane-1, 2-diol esters of fatty acids |
E 477 |
| Lactylated fatty acid esters of glycerol and propane-1, 2-diol |
-- |
| Sodium stearoyl-2-lactylate |
E 481 |
| Calcium stearoy1-2-lactylate |
E 482 |
| Stearyl tartrate |
E 483 |
| Polyoxyethylene (8) stearate |
-- |
| Polyoxyethylene (40) stearate |
-- |
| Polyoxyethylene (20) sorbitan |
|
| monostearate or polysorbate 60 |
-- |
| Polyoxyethylene (20) sorbitan |
|
| tristearate or polysorbate 65 |
-- |
| Polyoxyethylene (20) sorbitan |
|
| monopalmitate or polysorbate 40 |
-- |
| Polyoxyethylene (20) sorbitan |
|
| monolaurate or polysorbate 20 |
-- |
| Polyoxyethylene (20) sorbitan |
|
| mono-oleate or polysorbate 80 |
-- |
| Sorbitan monostearate |
-- |
| Sorbitan tristearate |
-- |
| Sorbitan monopalmitate |
-- |
| Sorbitan monolaurate |
-- |
| Sorbitan mono-oleate |
-- |
| Dioctyl sodium sulphosuccinate |
-- |
|
|
|
Restriction on use:
|
|
|
Restricted to the use of an amount not in excess of that required in accordance with good manufacturing practice unless otherwise specified in these Regulations.
|
|
|
PART II.
|
|
|
Specific Purity Criteria for permitted Emulsifiers and Stabilisers.
|
|
|
|
|
|
| E 322 Leicithins. |
| Chemical description: |
Leicithins are mixtures or fractions of phosphatides obtained by physical procedures from animal or vegetable foodstuffs. The lecithins may be slightly bleached in aqueous medium by means of hydrogen peroxide. This oxidation must not chemically modify the lecithin phosphatides. |
| Description: |
Brown liquid or viscous semi-liquid or powder. |
| Content: |
Not less than 60% substances insoluble in acetone. |
| Volatile matter: |
Not more than 2% determined by drying at 105°C for 1 hour. |
| Substances insoluble in Toluene: |
Not more than 0.3%. |
| Acid number: |
Not more than 35 mg potassium hydroxide per gramme. |
| Peroxide number: |
Equal to or less than 10, expressed as milliequivalents per kg. |
| Ammonium phosphatides. |
| Description: |
An unctuous semi-solid (at 25°C.) and consisting essentially of a mixture of the ammonium salts of phosphatidic acids derived from partially hardened rapeseed oil together with unreacted partially hardened rapeseed oil. |
| Matter insoluble in petroleum ether (40°C.-60°C.): |
Total: Not more than 2.5%.
Inorganic matter: Not more than 0.2%.
|
| pH of an aqueous extract of melted ammonium phosphatides: |
Not less than 6.0 and not more than 8.0. |
| Phosphorus: |
Not less than 3.0% and not more than 3.4%. |
| Ammonium nitrogen: |
Not less than 1.2% and not more than 1.5%. |
| Arsenic: |
Not more than 5 mg/kg. |
| E 339 A Monosodium orthophosphate. |
| Chemical description: |
Monosodium monophosphate; acid monosodium monophosphate; monosodium orthophosphate; monobasic sodium phosphate; Na H2PO4; the substance is available commercially in anhydrous or hydrated form with 1 or 2 molecules of water. |
| Description: |
Slightly deliquescent white powder, crystals or granules. |
| Content: |
Not less than 97% Na H2PO4 on a volatile matter-free basis. |
| Volatile matter: |
Determined by drying at 60°C for 1 hour and then at 105°C for 4 hours. |
|
--anhydrous: not more than 2%.
|
|
--with 1 molecule of water: not more than 15%.
|
|
--with 2 molecules of water: not more than 25%.
|
| Water-insoluble substances: |
Not more than 0.2% of the volatile matter-free substance. |
| Flourides: |
Not more than 10 mg/kg expressed as flourine. |
| E 339 B Disodium orthophosphate. |
| Chemical description: |
Disodium monophosphate; secondary sodium phosphate; disodium orthophosphate; acid disodium phosphate; Na2H PO4.
The substance is available commercially in anhydrous form or as a hydrate with 2, 7 or 12 molecules of water.
|
| Description: |
--Anhydrous: white hygroscopic powder.
|
|
--with 2 molecules of water: white crystalline solid.
|
|
--with 7 molecules of water: granular powder or white efflorescent crystals.
|
|
--with 12 molecules of water: white efflorescent powder or crystals.
|
| Content: |
Not less than 98% Na2HPO4 on a volatile matter-free basis. |
| Volatile matter: |
Determined by drying at 60°C for 1 hour and at 105°C for 4 hours. |
|
--anhydrous: not more than 5%.
|
|
--with 1 molecule of water: not more than 21%.
|
|
--with 7 molecules of water: not more than 50%.
|
|
--with 12 molecules of water: not more than 61%.
|
| Water-insoluble substances: |
Not more than 0.2% of the volatile matter-free substance. |
| Fluorides; |
Not more than 10 mg/kg expressed as fluorine. |
| E 339 C Trisodium orthophosphates. |
| Chemical description: |
Trisodium monophosphate; trisodium orthophosphate; Na3 PO4; the substance is available commercially in anhydrous form or as a hydrate with 1 or 12 molecules of water. |
| Description: |
White powder, crystals or granules. |
| Content: |
Not less than 97% Na3PO4 on a volatile matter-free basis. |
| Volatile matter: |
Determined by drying at 105°C for 1 hour, followed by calcination at 800°C ± 25°C for 30 minutes. |
|
--anhydrous: not more than 2%. |
|
--with 1 molecule of water: not more than 9%.
--with 12 molecules of water; not more than 55%.
|
| Water-insoluble substances: |
Not more than 0.2% of the volatile matter-free substance. |
| Fluorides: |
Not more than 10 mg/kg expressed as fluorine. |
| E 340 A Monopotassium orthophosphate. |
| Chemical description: |
Monopotassium monophosphate: acid monopotassium monophosphate: KH2PO4. |
| Description: |
Colourless crystals or white granular or crystalline powder, hygroscopic. |
| Content: |
Not less than 98% KH2PO4 on a volatile matter-free basis. |
| Volatile matter: |
Not more than 2% determined by drying at 105°C for 4 hours. |
| Water-insoluble substances: |
Not more than 0.2% of the volatile matter-free substance. |
| Fluorides: |
Not more than 10 mg/kg expressed as fluorine. |
| E 340 B Dipotassium orthophosphate. |
| Chemical description: |
Dipotassium monophosphate; secondary potassium phosphate; acid dipotassium orthophosphate; dipotassium phosphate; K2H PO4. |
| Description: |
Colourless or white granular deliquescent substance. |
| Content: |
Not less than 98% K2H PO4 on a volatile matter-free basis. |
| Volatile matter: |
Not more than 2% determined by drying at 105° for 4 hours. |
| Water-insoluble substances: |
Not more than 0.2% of the volatile matter-free substance. |
| Fluorides: |
Not more than 10 mg/kg expressed as fluorine. |
| E 340 C Tripotassium orthophosphate. |
| Chemical description: |
Tripotassium monophosphate; tripotassium orthophosphate; K3PO4; the substance is available commercially in anhydrous form or hydrated form, the most common being that with 1 molecule of water of crystallization. |
| Description: |
White hygroscopic crystals or granules. |
| Content: |
Not less than 97% K3PO4 on a volatile matter-free basis. |
| Volatile matter: |
Determined by drying at 105°C for 1 hour followed by calcination at 800°C ± 25°C for 30 minutes. |
|
--anhydrous: not more than 3%. |
|
--with one molecule of water: not more than 20%.
|
| Water-insoluble substances: |
Not more than 0.2% of the volatile matter-free substance. |
| Fluorides: |
Not more than 10 mg/kg expressed as fluorine. |
| E 341 A Monocalcium orthophosphate. |
| Chemical description: |
Monocalcium phosphate: CaH4 (PO4)2; available commercially in anhydrous form or as the monohydrate. |
| Description: |
Granular powder or white, deliquescent crystals or granules. |
| Calcium content: |
Anhydrous: not less than 23% and not more than 25% expressed as CaO. |
|
With one molecule of water:
not less than 22.2% and not more than 24.7% expressed as CaO.
|
| Volatile matter: |
Anhydrous: not less than 14% and not more than 15.5% determined after calcination at 800°C ± 25°C for 30 minutes. |
|
With one molecule of water:
not more than 0.6% determined by drying at 60°C for 3 hours.
|
| Fluorides: |
Not more than 30 mg/kg expressed as fluorine. |
| E 341 B Dicalcium orthophosphate. |
| Chemical description: |
Dibasic calcium phosphate: Dicalcium phosphate; Ca H PO4 available commercially in anhydrous and dihydrate form. |
| Description: |
Impalpable white powder. |
| Calcium content: |
Anhydrous: not less than 39% and not more than 42% expressed as CaO. |
|
With two molecules of water: not less than 31.9% and not more than 33.5% expressed as CaO. |
| Volatile matter: |
Determined by calcination at 800°C ± 25°C to constant weight. |
|
Anhydrous: not less than 7% and not more than 8.5%. |
|
Dihydrate: not less than 24.5% and not more than 26.5%. |
| Fluorides: |
Not more than 50 mg/kg expressed as fluorine. |
| E 400 Alginic acid. |
| Chemical description: |
Linear glycuronoglycan consisting mainly of beta (1-4) linked D-mannuronic and alpha (1-4) linked L-guluronic acid units in pyranose ring form. Hydrophilic colloidal carbohydrate extracted by the use of dilute alkali from various species of brown seaweeds. |
| Description: |
A nearly odourless, tasteless white to yellowish fibrous powder. |
| Content: |
Yields, on a volatile matter-free basis, not less than 20% and not more than 23% of carbon dioxide corresponding to not less than 91.0% and not more than 104.5% of alginic acid (equivalent weight 200). |
| Ash: |
Not more than 4% on a volatile matter-free basis determined at 600°C after drying at 105°C for 4 hours. |
|
Insoluble matter:
(in dilute NaOH)
|
Not more than 0.5%. |
| Volatile matter: |
Not more than 15% determined by drying at 105°C for 4 hours. |
|
Acid-insoluble ash:
(insoluble in approx. 3 N hydrochloric acid)
|
Not more than 0.5%. |
| E 401 Sodium alginate. |
| Chemical name: |
Sodium salt of alginic acid. |
| Description: |
Nearly odourless, tasteless white to yellowish fibrous or granular powder. |
| Content: |
Yields, on a volatile matter-free basis, not less than 18% and not more than 21% of carbon dioxide corresponding to not less than 90.8% and not more than 106.0% of sodium alginate (equivalent weight 222). |
| Ash: |
Not less than 18.0% and not more than 27.0% on a volatile matter-free basis determined at 600°C after drying at 105°C for 4 hours. |
|
Insoluble matter:
(in dilute NaOH)
|
Not more than 0.5%. |
| Volatile matter: |
Not more than 15% determined by drying at 105°C for 4 hours. |
|
Acid-insoluble ash:
(insoluble in approx. 3 N hydrochloric acid).
|
Not more than 0.5%. |
| E 402 Potassium alginate. |
| Chemical name: |
Potassium salt of alginic acid. |
| Description: |
Nearly odourless, tasteless white to yellowish fibrous or granular powder. |
| Content: |
Yields, on a volatile matter-free basis, not less than 16.5% and not more than 19.5% of carbon dioxide corresponding to not less than 89.2% and not more than 105.5% of potassium alginate (equivalent weight 238). |
| Ash: |
Not less than 23% and not more than 32% on a volatile matter-free basis determined at 600°C after drying at 105°C for 4 hours. |
|
Insoluble matter:
(in dilute NaOH)
|
Not more than 0.5%. |
| Volatile matter: |
Not more than 15% determined by drying at 105°C for 4 hours. |
|
Acid-insoluble ash:
(insoluble in approx. 3 N hydrochloric acid).
|
Not more than 0.5%. |
| E 403 Ammonium alginate. |
| Chemical name: |
Ammonium salt of alginic acid. |
| Description: |
White to yellowish fibrous or granular powder. |
| Content: |
Yields, on a volatile matter-free basis, not less than 18% and not more than 21% of carbon dioxide corresponding to not less than 88.7% and not more than 103.6% of ammonium alginate (equivalent weight 217). |
| Ash: |
Not more than 4% on a volatile matter-free basis determined at 600°C after drying at 105°C for 4 hours. |
|
Insoluble matter:
(in dilute NaOH)
|
Not more than 0.5%. |
| Volatile matter: |
Not more than 15% determined by drying at 105°C for 4 hours. |
|
Acid-insoluble ash:
(insoluble in approx. 3 N hydrochloric acid).
|
Not more than 0.5%. |
| E 404 Calcium alginate. |
| Chemical name: |
Calcium salt of alginic acid. |
| Description: |
Nearly odourless, tasteless fibrous or granular powder. |
| Content: |
Yields, on a volatile matter-free basis, not less than 18% and not more than 21% of carbon dioxide corresponding to not less than 89.6% and not more than 104.5% of calcium alginate (equivalent weight 219). |
| Ash: |
Not less than 15% and not more than 24% on a volatile matter-free basis determined at 600°C after drying at 105°C for 4 hours. |
| Insoluble matter (in dilute NaOH using sodium polyphosphate E 450 (c)): |
Not more than 0.5%. |
| Volatile matter: |
Not more than 15% when dried for 4 hours at 105°C. |
|
Acid-insoluble ash:
(insoluble in approx. 3 N hydrochloric acid).
|
Not more than 0.5%. |
| E 405 Propane-1, 2-diol alginate. |
| Chemical description: |
Propane-1,2-diol ester of alginic acid, varies in composition according to its degree of esterification and the percentages of free and neutralized carboxyl groups in the molecule. |
| Description: |
Nearly odourless and tasteless white to yellowish fibrous or granular powder. |
| Content: |
Yields, on a volatile matter-free basis, not less than 16% and not more than 20% of carbon dioxide. |
| Ash: |
Not more than 10% on a volatile matter-free basis determined at 600°C after drying at 105°C for 4 hours. |
| Total propane- 1,2-diol content: |
Not less than 15% and not more than 20%. |
| Free propane- 1,2-diol content: |
Not more than 12%. |
|
Insoluble matter:
(in dilute NaOH)
|
Not more than 0.5%. |
| Volatile matter: |
Not more than 20% when dried for 4 hours at 105°C. |
|
Acid-insoluble ash:
(insoluble in approx. 3 N hydrochloric acid).
|
Not more than 0.5%. |
| E 406 Agar. |
| Chemical description: |
A hydrophilic colloidal poly-galactoside, about 90% of the galactose molecules being of the D-form and 10% of the L-form. On about every tenth D-galactopyranose unit one of the hydroxyl groups is esterified with sulphuric acid which is neutralised by calcium, magnesium, potassium or sodium. It is extracted from certain marine algae of the families Gelidiaceae and Sphaerococcaceae and related red algae of the class Rhodophyceae. |
| Description: |
White to pale yellow powder, fibres or flakes which are either odourless, or have a slight characteristic odour and a mucilaginous taste. |
| Ash: |
Not more than 6.5% determined at 550°C on a volatile matter-free basis. |
|
Acid insoluble ash:
(insoluble in approx. 3N hydrochloric acid).
|
Not more than 0.5% at 550°C on a dryweight basis. |
| Gelatin and other proteins: |
Dissolve about 1 g agar in 100 ml of boiling water and allow to cool to about 50°C. To 5 ml. of the solution add 5 ml of trinitrophenol solution (1 g of anhydrous trinitrophenol/100 ml hot water). No turbidity appears within 10 minutes. |
|
Insoluble matter:
(in hot water)
|
Not more than 1%. |
| Volatile matter: |
Not more than 20% when dried for 5 hours at 105°C. |
| Starch and dextrins: |
Boil 100 mg agar in 100 ml of water. Cool and add a few drops of iodine solution prepared by dissolving 14 g I2 in a solution of 36 g K l in 100 ml. H2O. Add 3 drops HCL and dilute to 1,000 ml. No blue or red colour is produced. |
| Water absorption: |
Place 5 g agar in a 100 ml graduated cylinder, fill to the mark with water, mix and allow to stand at about 25°C for 24 hours. Pour the contents of the cylinder through moistened glass wool, allowing the water to drain into a second 100 ml graduated cylinder. Not more than 75 ml water is obtained. |
| E 407 Carrageenan. |
| Chemical description: |
Obtained by aqueous extraction of Seaweeds of gigartinaceae, solieriaceae, hypneaceae, furcellariaceae and families of the class rhodophyceae (red seaweeds). No organic precipitants shall be used other than methanol, ethanol and isopropanol. Carrageenan consists chiefly of the calcium, potassium, sodium, and magnesium salts of polysaccharide sulphate esters which, on hydrolysis, yield galactose and 3, 6 anhydrogalactose. Carrageenan shall not be hydrolysed or otherwise chemically degraded. |
| Description: |
Yellowish to colourless, coarse to fine powder which is practically odourless and has a mucilaginous taste. |
| Volatile matter: |
Not more than 12% determined by drying at 105°C for 4 hours. |
|
Sulphate:
(expressed as SO4)
|
Not less than 15% and not more than 40%. on a volatile matter-free basis, expressed as SO4 |
|
Acid insoluble ash:
(insoluble in approx.
1% v/v sulphuric acid)
|
Not more than 2% on a volatile matter-free basis. |
| Ash: |
Not less than 15% and not more than 40% determined at 550°C on a volatile matter-free basis. |
| Viscosity of a 1.5% solution at 75°C |
Not less than 5 centipoises. |
|
Isopropanol
Ethanol
Methanol
Content
|
} |
Not more than 1% singly or in combination.
|
| E 410 Locust bean gum |
| Chemical description: |
Consists mainly of a high molecular weight hydrocolloidal polysaccharide composed of galactopyranose and mannopyranose units combined through glycosidic linkages, which may be described chemically as galactomannan. |
| Description: |
The ground endosperm of the seeds of the carob tree. Geratonia Siliqua (L) Taub. (Fam. Leguminosae). |
|
A white to yellowish-white nearly odourless powder. |
| Galactopyranose and mannopyranose content: |
Not less than 75%. |
|
Insoluble matter:
(in 0.4 N Sulphuric acid)
|
Not more than 4% after digestion for 6 hours. |
| Ash: |
Not more than 1.2% determined at 800°C. |
| Volatile matter: |
Not more than 14% when dried to constant weignt at 102°--105° C (3--5 hours). |
| Protein (N x 6.25): |
Not more than 7%. |
| E 412 Guar gum |
| Chemical description: |
Consists mainly of a high molecular weight hydrocolloidal polysaccharide, composed of galactopyranose and mannopyranose
units combined through glycoside linkages, which may be described chemically as galactomannan.
|
| Description: |
The ground endosperm of the seeds of the guar plant, Cyamopsis tetragonolobus (L) Taub. (Fam, Leguminosae). A white to yellowish-white nearly odourless powder. |
| Galactopyranose content: |
Not less than 75%. |
|
Insoluble matter:
(in 0.4 N sulphuric acid)
|
Not more than 4% after digestion for 6 hours. |
| Ash: |
Not more than 1.5% determined at 800°C. |
| Volatile matter: |
Not more than 14% when dried to constant weight at 102°--105°C. (3--5 hours). |
| Protein (N x 6.25): |
Not more than 7%. |
| E 413 Tragacanth |
| Chemical description: |
Consists mainly of high molecular weight polysaccharides composed of galacto-arabans and acidic polysaccharides containing galacturonic acid groups. |
| Description: |
A dried gummy exudate obtained from Astragalus gummifer Labillardiere, or other Asiatic species of Astragulus (Fam. Leguminosae). Unground tragacanth occurs as flattened, lamellated, frequently curbed fragments or straight or spirally twisted linear pieces from 0.5 to 2.5 mm in thickness which are white to pale yellow in colour. It is odourless and has an insipid, mucilaginous taste. |
|
Powdered tragacanth is white to yellowish-white in colour. |
| Viscosity of a 1% solution at 25°C: |
Not less than 250 centipoises |
| Ash: |
Not more than 3.5% at 550°C. |
|
Acid-insoluble ash:
(insoluble in approx. 3 N hydrochloric acid).
|
Not more than 0.5% at 550°C. |
| Karaya gum: |
Boil 1 g with 20 ml of water until a mucilage is formed. Add 5 ml of hydrochloric acid and again boil the mixture for 5 minutes. No permanent pink or red colour develops. |
| E 414 Acacia |
| Chemical description: |
Consists mainly of high molecular weight polysaccharides and their calcium, potassium and magnesium, which on hydrolysis yield salts arabinose. galactose, rhamnose andglycuronic acid. It is obtained as a dried gummy exudate from the stems and branches of Acacia senegal (L) Willd or of related species of Acacia (Fam. Leguminosae). |
| Description: |
Unground acacia occurs as white, yellowish-white or pale pinkish spheroidal tears of varying size or in angular fragments. It is also available commercially in the form of white or yellowish-white flakes, granules or powder. |
| Ash: |
Not more than 4% at 550°C. |
|
Acid(insoluble ash:
in approx. 3 N hydrochloric acid):
|
Not more than 0.5% at 550°C. |
|
Insoluble matter:
(in approx. 3 N hydrochloric acid).
|
Not more than 1%. |
| Volatile matter: |
Not more than 15% determined by drying at 105°C for 5 hours. |
| Starch or dextrin: |
Boil a 1 in 50 solution of the gum and cool. To 5 ml. add one drop of iodine solution (14 g iodine in a solution of 36g potassium iodine in 100 ml water, add 3 drops hydrochloric acid and dilute to 1.000 ml). No bluish or reddish colour is produced. |
| Tannin: |
To 10 ml of a 1 in 50 solution add about 0.1 ml of ferric chloride solution (9 g FeCl3· 6H2O made up to 100 ml with water). No blackish colouration or blackish precipitate is formed. |
| E 420 (i) Sorbitol |
| Chemical name: |
D-sorbitol. |
| Description: |
White hygroscopic crystalline powder, flakes or granules, having a sweet taste. |
| Content: |
Sorbitol contains not less than 98% of glycitols and not less than 91% of D-sorbitol, on a dry matter basis in each case. Glycitols are compounds with the structural formula CH2OH(CHOH)nCH2OH where 'n' is an integer. That part of the product which is not D-sorbitol is composed mainly of mannitol together with small quantities of other glycitols, x ≤ 4, and minor quantities of hydrogenated oligosaccharides. |
| Water: |
Not more than 10% (Karl Fischer). |
| Reducing sugars: |
Not more than 0.3% on a dry-weight basis, expressed as dextrose. |
| Total sugars: |
Not more than 1% on a dry-weight basis, expressed as dextrose. |
| Sulphated ash: |
Not more than 0.1% at 800 ± 25°C on a dry-weight basis. |
| Sulphate: |
Not more than 0.01% on a dry-weight basis. |
| Chloride: |
Not more than 0.005% on a dry-weight basis, expressed as C1. |
| Nickel: |
Not more than 2 mg/kg. expressed as Ni. |
| (ii) Sorbitol Syrup |
|
| Description: |
Clear colourless and sweet-tasting aqueous solution of sorbitol and hydrogenated oligosaccharides. That part of the product which is not D-sorbitol is composed mainly of hydrogenated oligosaccharides formed by the hydrogenation of glucose syrup used as raw material (in which case the syrup is non-crystallising) or mannitol. Minor quantities of other glycitols where n ≤ 4 may be present. |
| Content: |
Not less than 69% total solids and not less than 50% of D-sorbitol. |
| Sulphated ash: |
Not more than 0.1% on a dry-weight basis. |
| Sulphate: |
Not more than 0.01% on a dry-weight basis. |
| Chloride: |
Not more than 0.005% on a dry-weight basis. |
| Nickel: |
Not more than 2 mg/kg. |
| Reducing sugars: |
Not more than 0.3% on a dry-weight basis, expressed as dextrose. |
| E 421 Mannitol |
| Chemical name: |
D-mannitol. |
| Description: |
White crystalline solid which is odourless and has a sweet taste. |
| Content: |
Not less than 98% of D-mannitol (C6H14O6) on a volatile matter-free basis. |
| Melting range |
165°C-168°C. |
|
Specific rotation
[∝] 25
D
|
Not less than +23.0° and not more than +24.3°. |
| Volatile matter: |
Not more than 0.3% determined by drying at 105°C for 4 hours. |
| Reducing sugars: |
Not more than 0.05% expressed as dextrose. |
| Sulphate: |
Not more than 0.01%, expressed as SO4. |
| Chloride: |
Not more than 0.007%, expressed as C1. |
| Ash: |
Not more than 0.1% determined at 800 ± 25°C. |
| Nickel: |
Not more than 2 mg/kg, expressed as Ni. |
| E 422 Glycerol |
| Chemical name: |
Glycerol. |
| Description: |
Clear, colourless hygroscopic syrupy liquid with a sweet taste accompanied by a sensation of heat to the tongue. |
| Content: |
Not less than 98% of glycerol (C3H8O3). |
| Specific gravity: (25/25°C) |
Not less than 1.257. |
|
Refractive index:
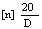
Acrolein, glucose and ammonium compounds:
|
1.471-1.474.
Heat a mixture of 5 ml glycerol and 5 ml potassium hydroxide solution (1 in 10) at 60°C for 5 minutes. It neither becomes yellow nor emits an odour of ammonia.
|
| Butanetriols: |
Not more than 0.2%. |
| Chlorinated compounds: (as C1) |
Not more than 0.003%. |
| Fatty acids and esters: |
Not more than 0.1% calculated as butyric acid. |
| Sulphated ash: |
Not more than 0.01% determined at 800 ± 25°C. |
| E 440 (A) Pectin |
| Chemical description: |
Pectins consist mainly of the partial methyl esters of polygalacturonic acid and their sodium, potassium, calcium and ammonium salts. Pectin is obtained by aqueous extraction of appropriate edible plant material, usually citrus fruits or apples. No organic precipitants shall be used other than methanol, ethanol and isopropanol. |
| Description: |
White, light yellow, light grey or light brown powder. |
| Galacturonic acid: |
Not less than 65% calculated on an ash and volatile matter-free basis after washing with acid and alcohol. |
| Volatile matter: |
Not more than 12% after drying at 105°C for 2 hours. |
|
Acid-insoluble ash:
(insoluble in approx. 3 N hydrochloric acid)
|
Not more than 1% |
| Free methanol, ethanol and isopropanol content: |
Not more than 1% singly or in combination on a volatile matter-free basis. |
| Sulphur dioxide residue: |
Not more than 50 mg/kg on a volatile matter-free basis. |
| Nitrogen content: |
Not more than 0.5% determined after washing with acid and alcohol [kjeldahl]. |
| E 440 (B) Amidated Pectin |
| Chemical description: |
Amidated Pectins consist mainly of the partial methyl esters and amides of polygalacturonic acid and their ammonium sodium, potassium and calcium salts.
It is obtained by aqueous extraction of appropriate edible plant material. usually citrus fruits or apples and treatment with ammonia under alkaline conditions. No organic precipitants shall be used other than methanol, ethanol and isopropanol.
|
| Description: |
White, light yellow, light grey or light brown powder. |
| Degree of amidation: |
Not more than 25% of total carboxyl groups. |
| Galacturonic acid: |
Not less than 65% calculated on an ash and volatile matter-free basis determined after washing with acid and alcohol. |
| Volatile matter: |
Not more than 12% after drying at 105°C for 2 hours. |
|
Acid-insoluble ash:
(insoluble in approx. 3 N hydrochloric acid)
|
Not more than 1%, |
| Free methanol, ethanol and isopropanol content: |
Not more than 1% singly or in combination on a volatile matter-free basis. |
| Sulphur dioxide residue: |
Not more than 50 mg/kg on a volatile matter-free basis. |
| Nitrogen content: |
Not more than 2.5% after washing with acid and alcohol [kjeldahl). |
| Ghatti gum |
| Description: |
An off-white to buff powder. A complex high molecular weight polysaccharide derived from the gum exuded from the stem of the tree Anogeissus latifolia. |
| Solubility: |
Completely soluble in five parts of water forming a very viscous mucilage. Insoluble in ethanol. |
| Identification: |
On acid hydrolysis the gum yields L-arabinose. D-galactose, D-mannose, D-xylose and D-glucuronic acid. |
|
Precipitates from ghatti gum solutions are characterised as follows: |
|
Reagent
Ethanol (90% aqueous solution)
|
Precipitate
Fine, flocculent non-adherent
|
|
Tannic acid (10% aqueous solution) |
Precipitate (distinction from Acacia) |
|
Lead acetate (20% aqueous solution) |
None (distinction from Amrad and other gums) |
|
Lead sub- acetate solution (Basic lead acetate) |
Translucent flocculent |
|
Potassium hydroxide (10% aqueous solution) |
None |
|
Ferric chloride (5% aqueous solution) |
None (absence on tannin) |
|
diSodium tetraborate (4% aqueous solution) |
None |
| Moisture: |
Not more than 14% [Karl Fischer]. |
| Ash: |
Total: Not more than 3 per cent on a moisture-free basis. |
|
Acid insoluble: Not more than 0.35% on a moisture free basis (using approx. 2 N HC 1). |
| Starch or dextrins: |
Addition of a few drops of iodine solution to an aqueous solution of ghatti gum shall not produce a blue or reddish colouration. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Karaya gum or Sterculia Gum
|
|
|
The criteria in the monograph for karaya gum contained in the Food Chemicals Codex 1972 at page 423.
|
|
|
Xanthan gum
|
|
|
The criteria in the monograph for xanthan gum contained in the Food Chemicals Codex 1972 page 856 with the additional requirements that viable cells of Xanthomonas campostris shall be absent and that the nitrogen content shall be not more than 1.5%.
|
|
|
E 450 (a) (i) diSodium dihydrogen diphosphate (Na2H2P2O7) or Sodium acid salt of pyrophosphoric acid
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Description: |
White powder or grains. |
| Content: |
Not less than 95% of Na2H2P2O7. |
| Content in P2O5: |
Not less than 63.0% and not more than 64.0%. |
| Loss on drying: |
Not more than 0.5% after drying for 4 hours at 105°C. |
| pH of 1% solution: |
Not less than 3.7 and not more than 4.4. |
| Water insoluble matter: |
Not more than 0.6%. |
| Fluoride: |
Not more than 10 mg/kg. expressed as fluorine. |
|
|
|
E 450 (a) (ii) Trisodium diphosphate (Na3HP2O7) or sodium pyrophosphate
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Description: |
White powder or grains, Occurs anhydrous or as a monohydrate. |
| Content: |
Not less than 95% of Na3HP2O7 or of Na3HP2O7H2O. |
| Content in P2O5: |
Not less than 57.5% and not more than 58.5% for the anhydrous salt. Not less than 53.6% and not more than 54.6% for the monohydrate. |
| pH of a 1% solution: |
Not less than 6.7 and not more than 7.3. |
| Volatile matter: |
Not more than 0.5% determined by drying at 105°C for 4 hours. |
| Water insoluble matter: |
Not more than 0.2%. |
| Fluoride: |
Not more than 10 mg/kg, expressed as fluorine. |
|
|
|
E 450 (a) (iii) Tetrasodium diphosphate (Na4P2O7) or tetra sodium pyrophosphate
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Description: |
White, crystalline or granular powder. Occurs anhydrous or as a decahydrate. |
| Content: |
Not less than 95% of Na4P2O7 or of Na4P2O7H2O. |
| Content in P2O5: |
Not less than 52.5% and not more than 54.0% for the anhydrous salt. |
|
Not less than 31.5% and not more than 32.5% for the decahydrate. |
| Loss on ignition: |
Not more than 0.5% for the anhydrous salt, not less than 38% and not more than 42% for the decahydrate, in both cases determined after drying at 105°C for 4 hours, followed by ignition at 550°C for 30 minutes. |
| pH of a 1% solution: |
Not less than 9.9 and not more than 10.7 |
| Water insoluble matter: |
Not more than 0.2%. |
| Flouride: |
Not more than 10 mg/kg, expressed as fluorine. |
|
|
|
E 450 (a) (iv) Tetrapotassium diphosphate (K4P2O7) or potassium pyrophosphate
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Description: |
Colourless crystals or white, very hygroscopic powder. |
| Content: |
Not less than 95% of K4P2O7. |
| Content in P2O5: |
Not less than 42.0% and not more than 43.7%. |
| Loss on ignition: |
Not more than 2% after drying for 4 hours at 105°C followed by ignition at 550°C for 30 minutes. |
| pH of a 1% solution: |
Not less than 10.0 and not more than 10.7. |
| Water insoluble matter: |
Not more than 0.2%. |
| Fluoride: |
Not more than 10 mg/kg. expressed as fluorine. |
|
|
|
E 450 (b) (i) Pentasodium triphosphate (Na5P3O10) or sodium tripolyphosphate
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Description: |
White, slightly hygroscopic granules or powder. Occurs anhydrous or as an hexahydrate. |
| Content: |
Not less than 85.0% of Na5P3O10 or of Na5P3O106H2O remainder being principally other sodium phosphates (E450). |
| Content in P2O5: |
Not less than 56.0% and not more than 58.0% for the anhydrous salt. Not less than 43.0% and not more than 45.0% for the hexahydrate. |
| Loss on ignition: |
For the anhydrous salt not more than 0.5% and for the hexahydrate not more than 23.2% in both cases determined after drying for 4 hours at 105°C followed by ignition at 550°C for 30 minutes. |
| pH of a 1% Solution: |
Not less than 9.3 and not more than 10.1. |
| Water insoluble matter: |
Not more than 0.2%. |
| Fluoride: |
Not more than 10 mg/kg, expressed as fluorine. |
|
|
|
E 450 (b) (ii) Pentapotassium triphosphate (K5P3O10)
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Description: |
White, very hygroscopic powder. |
| Content: |
Not less than 85% of K5P3O10 after ignition at 550°C for 30 minutes, the remainder being principally other potassium phosphates (E450). |
| Content in P2O5: |
Not less than 46.5% and not more than 48.0%. |
| Loss on ignition: |
Not more than 0.5% calculated on the P2O5 content after drying for 4 hours at 105°C followed by ignition at 550°C for 30 minutes. |
| pH of a 1% solution: |
Not less than 9.3 and not more than 10.1. |
| Water insoluble matter: |
Not more than 0.2%. |
| Fluoride: |
Not more than 10 mg/kg, expressed as fluorine. |
|
|
|
E 450 (c) (i) Sodium polyphosphates
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Chemical description: |
Heterogenous mixtures of sodium salts of linear condensed polyphosphoric acids of general formula H(n+2)PnO(3n+1) where 'n' is not less than 2. |
| Description: |
Fine white powders or crystals or colourless glassy platelets. |
| Content in P2O5: |
Not less than 59.5% and not more than 70.0% calculated on the ignited basis. |
| Loss on ignition: |
Not more than 0.5% after drying at 105°C for 4 hours followed by ignition at 550°C for 30 minutes. |
| pH of a 1% solution: |
Not less than 3.6 and not more than 9.0. |
| Water insoluble matter: |
Not more than 0.2%. |
| Fluoride: |
Not more than 10mg/kg, expressed as fluorine. |
| Cyclic phosphates: |
Not more than 8%. |
|
|
|
E 450 (c) (ii) Potassium polyphosphates
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Chemical description: |
Heterogenous mixtures of potassium salts of linear condensed polyphosphoric acids of general formula H(n + 2)PnO(3n + 1) where 'n' is not less than 2. |
| Description: |
Fine white powders or crystals or colourless glassy platelets. |
| Content in P2O5: |
Not less than 53.5% and not more than 61.5% on the ignited basis. |
| Loss on ignition: |
Not more than 2% after drying for 4 hours at 105°C followed by ignition at 550°C for 30 minutes. |
| pH of a 1% solution: |
Not more than 7.8. |
| Water insoluble matter: |
Not more than 0.2%. |
| Fluoride: |
Not more than 10 mg/kg, expressed as fluorine. |
| Cyclic phosphates: |
Not more than 8%. |
| E 460 Microcrystalline cellulose |
| Chemical description: |
Purified partially depolymerised cellulose prepared by acid hydrolysis of alpha-cellulose obtained directly from fibrous plant material. It has a molecular weight of about 36,000. |
| Description: |
A fine white or almost white odourless powder. |
| Volatile matter: |
Not more than 5% determined by drying to constant weight at 105°C. |
| pH: |
Shake about 5 g with 40 ml of carbon dioxide free water for 20 minutes and centrifuge. The pH of the supernatant liquid is between 5.5 and 7.0. |
| Sulphated ash: |
Not more than 0.1% determined at 800 2± 5°C. |
| Water soluble substances: |
Not more than 0.16%. |
| Diethyl ether extractable matter: |
Not more than 200 mg/kg. |
| Chloride: |
Not more than 350 mg/kg expressed as C1. |
| Sulphate: |
Not more than 600 mg/kg expressed as SO4. |
| E 461 Methylcellulose |
| Chemical description: |
Obtained directly from fibrous plant material and partially etherified with methyl groups. |
| Description: |
A slightly hygroscopic white or slightly yellowish or greyish odourless and tasteless granular or fibrous powder. |
| Chemical formula: |
The polymers contain substituted glucose units with the following general formula: |
|
C6H7O2 (OR1) (OR2) (OR3) where R1, R2, and R3 each may be
--H
--CH3 or
--CH2CH2OH.
|
| Molecular weight: |
From about 20,000 to 380,000. |
| Content of substituted groups: |
Not less than 25% and not more than 33% of methoxyl-groups (--OCH3). No more than 5% of hydroxyethoxyl groups (--OCH2CH2OH). |
| Volatile matter: |
Not more than 10% determined by drying to constant weight at 105°C, |
| Sulphated ash: |
Not more than 1.5% determined at 800 ± 25°C. |
| pH of a 1% solution: |
Not less than 5 and not more than 8. |
| E 463 Hydroxypropylcellulose |
|
| Chemical Description: |
Obtained directly from fibrous plant material and partially etherified with hydroxypropyl group. |
| Description: |
Slightly hygroscopic white or slightly yellowish or greyish odourless and tasteless, granular or fibrous powder. |
| Chemical formula: |
The polymers contain substituted glucosidic units with the following general formula: |
|
C6H7O2 (OR1) (OR2) (OR3) where R1, R2 and R3 each may be any one of the following: |
|
--H
--CH2 CHOHCH3
--CH2 CHO (CH2 CHOHCH3) CH3
--CH2 CHO [CH2CHO(CH2 CHOHCH3)CH3]CH3
|
| Molecular weight: |
From about 30,000 to 1,000,000. |
| Content of substituted groups: |
Not more than 80.5% of hydroxypropoxyl groups (--OCH2 CHOHCH3) on a volatile matter-free basis, equivalent to not more than 4.6 hydroxypropyl groups per anhydroglucose unit. |
| pH of a 1% solution: |
Not less than 5.0 and not more than 8.0. |
| Volatile matter: |
Not more than 10% determined by drying to constant weight at 105°C. |
| Sulphated ash: |
Not more than 0.5% determined at 800 ± 25°C. |
| E 464 Hydroxypropylmethylcellulose |
| Chemical description: |
Obtained directly from fibrous plant material and partially etherified with methyl groups and containing a small degree of hydroxypropyl substitution. |
| Description: |
Slightly hygroscopic white or slightly yellowish or greyish odourless and tasteless, granular or fibrous powder. |
| Chemical formula: |
The polymers contain substituted anhydroglycose units with the following general formula: |
|
C6H7O2 (OR1) (OR2) (OR3) where R1, R2 and R3 each may be any one of the following: |
|
--H
--CH3
--CH2CHOHCH3
--CH2CHO (CH2CHOHCH3) CH3
--CH2CHO [CH2CHO (CH2 CHOHCH3)CH3]CH3
|
| Molecular weight: |
From about 13,000 to 200,000. |
| Content of substituted groups: |
Not less than 19% and not more than 30% of methoxyl groups (--OCH3) and not less than 3% and not more than 12% hydroxypropoxyl groups (--OCH2CHOHCH3) on a volatile matter-free basis. |
| pH of a 1% solution: |
Not less than 5.0 and not more than 8.0. |
| Volatile matter: |
Not more than 10% after drying to constant weight at 105°C. |
| Sulphated ash: |
Not more than 1.5% for products with viscosities greater than 50cP and not more than 3.0% for products with viscosities of 50cP or less, determined at 800 ± 25°C. |
| E 465 Ethylmethylcellulose. |
|
| Chemical description: |
Obtained directly from fibrous plant material and partially etherified with methyl and ethyl groups. |
| Description: |
Slightly hygroscopic white or slightly yellowish or greyish odourless and tasteless granular or fibrous powder. |
| Chemical formula: |
The polymers contain substituted anhydroglucose units with the following general formula: |
|
C6H7O2 (OR1) (OR2) (OR3) where R1, R2, and R3 each may be any one of the following |
|
--H
--CH3
--CH2CH3
|
| Molecular weight: |
From about 30,000 to 40,000. |
| Content of substituted groups: |
Not less than 14.5% and not more than 19% of ethoxyl groups (--OC2H5) and not less than 3.5% and not more than 6.5% of methoxyl groups (--OCH3) on a volatile matter-free basis. |
| Volatile matter: |
Fibrous form: not more than 15%. Powdered form: not more than 10%. Determined by drying to constant weight at 105°C in each case. |
| Sulphated ash: |
Not more than 0.6% determined at 800 ± 25°C. |
| pH of a 1% solution: |
Not less than 5 and not more than 8. |
| E 466 Carboxymethylcellulose. |
|
| Chemical description: |
The partial sodium salt of a carboxymethyl ether of cellulose, the cellulose being obtained directly from fibrous plant material. |
| Description: |
Slightly hygroscopic white or slightly yellowish or greyish, odourless and tasteless, granular or fibrous powder. |
| Chemical formula: |
The polymers contain substituted glucosidic units with the following general formula: |
|
C6H7O2 (OR1) (OR2) (OR3) where R1, R2 and R3 each may be any one of the following: |
|
--H
--CH2 COONa
--CH2 COOH
|
| Molecular weight: |
From about 17,000 to 500,000. |
| Content: |
Not less than 99.5% of carboxymethylcellulose calculated on a volatile matter-free basis. |
| Sodium chloride and sodium glycolate: |
Not more than 0.5% total and not more than 0.4% of sodium glycolate. |
| Degree of substitution: |
Not less than 0.2 and not more than 1.0 carboxymethyl groups (CH2 COOH) per anhydroglucose unit. |
| Sodium: |
Not more than 9.7% on a volatile matter-free basis. |
| Volatile matter: |
Not more than 12% determined by drying to constant weight at 105°C. |
| pH of a 1% Solution: |
Not less than 6 and not more than 8.5. |
| E 470 Sodium, Potassium and Calcium salts of food fatty acids. |
| Chemical description: |
Sodium, potassium and calcium salts of fatty acids occurring in food oils and fats, these salts being obtained either from edible fats or from distilled food fatty acids. |
| Description: |
White or creamy white light powders, flakes or semi-solids. |
| Unsaponifiable matter |
Not more than 2%. |
| Free fatty acids: |
Not more than 3% estimated as oleic acid. |
| Free alkali: |
Not more than 0.1% expressed as NaOH. |
| Total glycerol (combined and free): |
Not more than 1%. |
| Matter insoluble in alcohol: |
Not more than 0.2% (sodium and potassium salts only). |
| Loss on drying: |
Not more than 3% |
| Content of sodium or potassium or calcium: |
Sodium: 9% to 14% expressed as Na2O.
Potassium: 13% to 21.5% expressed as K2O.
Calcium: 8.5% to 13% expressed as CaO.
|
| E 471 Mono- and di-glycerides of food fatty acids. |
| Chemical description: |
Mixtures of glycerol mono-, di- and tri-esters of fatty acids occuring in food fats. They may contain amounts of free fatty acids and glycerol. |
| Description: |
The product varies from a pale straw to brown oily liquid to a white or slightly off-white hard waxy solid. These solids may be in the form of flakes, powders or small beads. |
| Mono-and di-Ester content: |
Not less than 70%. |
| Free fatty acids: |
Not more than 3% estimated as oleic acid. |
| Free glycerol: |
Not more than 7%. |
| Total glycerol: |
Not less than 16% and not more than 33%. |
| Polyglycerols: |
Not more than 4% diglycerol and not more than 1% higher polyglycerols both based on total glycerol content. |
| Water: |
Not more than 2% (Karl Fischer). |
| Sulphated ash: |
Not more than 0.5% determined at 800 ± 25°C. |
|
|
|
Note: These criteria are based on the product without E470.
|
|
|
E 472(a) Acetic acid esters of mono- and di-glycerides of fatty acids.
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Chemical description: |
Esters of glycerol with acetic acid and fatty acids occuring in food fats. They may contain small amounts of free glycerol, free fatty acids, free acetic acid, and free glycerides. |
| Description: |
Clear mobile liquids to solids and white to pale yellow in colour. |
| Total acetic acid content: |
Not less than 9% and not more than 32%. |
| Free fatty acids: (and acetic acid) |
Not more than 3% estimated as oleic acid. |
| Free glycerol: |
Not more than 2%. |
| Total glycerol: |
Not less than 14% and not more than 31%. |
| Sulphated ash: |
Not more than 0.5% determined at 800 ± 25°C. |
|
|
|
E 472(b) Lactic Acid esters of mono- and di-glycerides of food fatty acids.
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Chemical description: |
Esters of glycerol with lactic acid and forming fatty acids occuring in food fats. They may contain small amounts of free glycerol, free fatty acids, free lactic acid, and free glycerides. |
| Description: |
Soft to hard waxy solids. |
| Total lactic acid content: |
Not less than 13% and not more than 45%. |
| Free fatty acids: |
Not more than 3% estimated as oleic acid. |
| Free glycerol: |
Not more than 2%. |
| Total glycerol: |
Not less than 13% and not more than 30%. |
| Sulphated ash: |
Not more than 0.5% determined at 800 ± 25°C. |
|
|
|
Note: These criteria are based on the product without E 470.
|
|
|
E 472(c) Citric acid esters of mono- and di-glycerides of food fatty acids.
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Chemical description: |
Esters of glycerol with citric acid and fatty acids occuring in food fats. They may contain small amounts of free glycerol, free fatty acids, free citric acid and free glycerides. They may be partially or wholly neutralised with sodium hydroxide or with potassium hydroxide. |
| Description: |
Yellowish or light brown liquids to waxy solids or semi-solids. |
| Total citric acid content: |
Not less than 13% and not more than 50%. |
| Free fatty acids: |
Not more than 3% estimated as oleic acid. |
| Free glycerol: |
Not more than 2%. |
| Total glycerol: |
Not less than 11% and not more than 29%. |
| Sulphated ash: |
Not more than 0.5% for the non-neutralised products and not more than 10.0% for the partially or wholly neutralised products determined at 800 ± 25°C. |
| pH of a 1% solution: |
Not less than 3 and not more than 7.3. |
|
|
|
E 472(d) Tartaric acid esters of mono- and di-glycerides of food fatty acids.
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Chemical description: |
Esters of glycerol with tartaric acid (E334) and fatty acids occurring in food fats. They may contain small amounts of free glycerol, free fatty acids, free tartaric acid, and free glycerides. |
| Description: |
Sticky viscous yellowish liquids to hard yellow waxes. |
| Total tartaric acid content: |
Not less than 15% and not more than 50%. |
| Free fatty acids: |
Not more than 3% estimated as oleic acid. |
| Free glycerol: |
Not more than 2%. |
| Total glycerol: |
Not less than 12% and not more than 29%. |
| Sulphated ash: |
Not more than 0.5% determined at 800 ± 25°C. |
|
|
|
E 472(e) Mono-and diacetyl tartaric and esters of mono and di-glycerides of fatty acids.
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Chemical description: |
Esters of glycerol with mono- and diacetyl tartaric acids (obtained from E334 tartaric acid) and fatty acids occuring in food fats. They may contain small amounts of free glycerol, free fatty acids, free tartaric and acetic acid and their combinations, and free glycerides. |
| Description: |
Sticky viscous liquids through to fat-like consistency to yellow waxes which hydrolyse in moist air to liberate acetic acid. |
| Total tartaric acid content: |
Not less than 10% and not more than 40%. |
| Total acetic acid content: |
Not less than 8% and not more than 32%. |
| Free fatty acids: |
Not more than 3% estimated as oleic acid. |
| Free glycerol: |
Not more than 2%. |
| Total glycerol: |
Not less than 11% and not more than 28%. |
| Sulphated ash: |
Not more than 0.5% determined at 800 ± 25°C. |
|
|
|
E 472(f) Mixed acetic and tartaric acid esters of mono- and di-glycerides of fatty acids.
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Chemical description: |
Esters of glycerol with acetic and tartaric acids (E 334) and fatty acids occuring in food fats. They may contain small amounts of free glycerol, free fatty acids, free acetic and tartaric acids, and free glycerides. |
| Description: |
Clear mobile liquids to solids and from white to pale yellow in colour. |
| Total acetic acid: |
Not less than 10% and not more than 20%. |
| Total tartaric acid: |
Not less than 20% and not more than 40%. |
| Free acetic acid: |
Not less than 5.5% and not more than 8.5%. |
| Free tartaric acid: |
Not more than 1%. |
| Free fatty acids: |
Not more than 3% estimated as oleic acid. |
| Free glycerol: |
Not more than 2%. |
| Total glycerol: |
Not less than 12% and not more than 27%. |
| Sulphated ash: |
Not more than 0.5% determined at 800 ± 25°C. |
|
|
|
E 473 Sucrose esters of food fatty acids.
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Chemical description: |
Essentially the mono- and di-esters of sucrose with fatty acids occuring in food fats. They may be prepared from sucrose and the methyl and ethyl esters of food fatty acids or by extraction from sucroglycerides. No organic solvents shall be used in their preparation other than dimethylformamide, ethyl acetate and isopropanol. |
| Description: |
Soft solids, stiff gels or white to greyish-white powders. |
| Total sucrose fatty acid ester content: |
Not less than 80%. |
| Total glyceride content: |
Not more than 20%. |
| Free sucrose content: |
Not more than 5%. |
| Free fatty acid content: |
Not more than 3% estimated as oleic acid. |
| Sulphated ash: |
Not more than 2% determined at 800 ± 25°C. |
| Methanol content: |
Not more than 10 mg/kg. |
| Dimethyl formamide content: |
Not more than 1 mg/kg. |
| Total ethyl acetate and isopropanol content: |
Not more than 350 mg/kg singly or in combination. |
|
|
|
Note: These criteria are based on the product without E 470.
|
|
|
E 474 Sucroglycerides.
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Chemical description: |
Produced by reacting sucrose with an edible fat or oil to produce a mixture of essentially mono- and di-esters of sucrose and fatty acids together with residual mono-, di-and tri-glycerides from that fat or oil. No organic solvents shall be used in their preparation other than dimethylformamide, ethyl acetate and isopropanol. |
| Description: |
Soft solid masses, still gels or white to off-white powders. |
| Total sucrose fatty acid ester content: |
Not less than 40% and not more than 60%. |
| Total glyceride content: |
Not less than 40% and not more than 60%. |
| Free sucrose content: |
Not more than 5%. |
| Free fatty acid content: |
Not more than 3% estimated as oleic acid. |
| Sulphated ash: |
Not more than 2% determined at 800 ± 25°C. |
| Dimethyl formamide content: |
Not more than 1 mg/kg. |
| Total ethyl acetate and isopropanol content: |
Not more than 350 mg/kg singly or in combination. |
| Methanol content: |
Not more than 10 mg/kg. |
|
|
|
Note: These criteria are based on the product without E 470.
|
|
|
E 475 Polyglycerol esters of non-polymerised food fatty acids.
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Chemical description: |
Produced by the esterification of polyglycerol with food fats or with fatty acids occurring in food fats. The polyglycerol moiety is predominantly di-, tri-, and tetra-glycerol and contains not more than 10% of polyglycerols equal to or higher than heptaglycerol. |
| Description: |
Yellow or light brown liquids or semi-solids. |
| Total fatty acid ester content: |
Not less than 90%. |
| Free fatty acids: |
Not more than 6% estimated as oleic acid. |
| Total glycerol and polyglycerol: |
Not less than 18% and not more than 60%. |
| Free glycerol and polyglycerol: |
Not more than 7%. |
| Sulphated ash: |
0.5% determined at 800 ± 25°C. |
|
|
|
Note: These criteria are based on the product without E 470.
|
|
|
Partial polyglycerol esters of polycondensed fatty acids of castor oil.
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Description: |
A highly viscous liquid at 25°C being essentially a complex mixture of the partial esters and ethers of polyglycerol with linearly interesterified (polycondensed) fatty acids derived from castor oil. The polycondensed castor oil fatty acids are prepared by condensation in the absence of oxygen and have an average of about 5 fatty acid residues per molecule. The polyglycerol moiety is predominantly di-, tri- and tetra-glycerol and contains not more than 10% of polyglycerols equal to or higher than heptaglycerol. |
| Refractive index, ND65°C: |
Not less than 1.4630 and not more than 1.4665. |
| Hydroxyl value: |
Not less than 80 and not more than 100. |
| Iodine value: |
Not less than 72 and not more than 103[Wijs]. |
| Acid value: |
Not more than 6 mg. KoH per g. |
|
|
|
Polyglycerol esters of dimerised fatty acids of soya bean oil.
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Description: |
A viscous oil obtained by the interesterification of polyglycerol with refined soya bean oil thermally polymerised in vacuo. The polyglycerol moiety is predominantly di-, tri- and tetra-glycerol and contains not more than 10 per centum of polyglycerols equal to or higher than heptaglycerol. |
| Urea non-adduct content of total fatty acid methyl esters: |
Not more than 65%. |
| Saponification value: |
Not less than 158 and not more than 175. |
| Iodine value: |
Not less than 78 and not more than 82 [Wijs]. |
| Hydroxyl value: |
Not less than 60 and not more than 70. |
| Acid value: |
Not more than 6 mg. KOH per g. |
|
|
|
Oxidatively polymerised soya bean oil.
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Description: |
A highly viscous liquid at 25°C obtained by blowing air into edible soya bean oil at a temperature not exceeding 250°C. |
| Combined oxidised fatty acids: |
Not more than 30%. |
| Urea non-adduct content of total fatty acid methyl esters: |
Not more than 42%. |
| Refractive index, ND40°C: |
Not less than 1.475 and not more than 1.485. |
| Saponification value: |
Not more than 220. |
| Iodine value: |
Not less than 75 and not more than 85 [Wijs]. |
| Hydroxyl value: |
Not less than 30 and not more than 70. |
| Acid value |
Not more than 6 mg. KOH per g. |
|
|
|
E 477 Propane-1, 2-diol esters of food fatty acids.
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Chemical description: |
Consists chiefly of mixtures of propane-1, 2-diol mono- and di-esters of fatty acids occuring in food fats. The alcohol moiety is exclusively propane-1, 2-diol together with dimer and traces of trimer. Organic acids other than food fatty acids are absent. |
| Description: |
Waxy white flakes, beads or solids. |
| Total fatty acid ester content: |
Not less than 85%. |
| Free propane-1,2-diol: |
Not more than 5%. |
| Dimer and trimer of propane-1, 2-diol: |
Not more than 4%. |
| Free fatty acids: |
Not more than 6% estimated as oleic acid. |
| Sulphated ash: |
Not more than 0.5% determined at 800 ± 25°C. |
| Total propane-1, 2-diol content: |
Not less than 11% and not more than 31%. |
|
|
|
Note: These criteria are based on the product without E470.
|
|
|
Lactylated fatty acid esters of glycerol and propane-1, 2-diol.
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Description: |
Off-white to light caramel coloured flakes obtained by reacting hardened vegetable oils or hardened animal fats (iodine values less than 2) firstly with propane-1, 2-diol and then with lactic acid. |
| Combined glycerol: |
Not more than 6%. |
| Combined propane-1,2-diol: |
Not more than 14%. |
| Combined lactic acid: |
Not more than 18%. |
| Saponification value: |
Not less than 230 and not more than 250 |
| Matter soluble in water: |
Not more than 5%. |
| Acid value: |
Not more than 12 mg. KOH per g. |
| E 481 Sodium Stearoyl-2- Lactylate. |
|
| Chemical description: |
A mixture of the sodium salts of stearoyl lactylic acids and minor amounts of sodium salts of other related acids, manufactured by the reaction of stearic acid and lactic acid. Other food fatty acids may also be present free or esterified due to their presence in the stearic acid used. |
| Description: |
Cream coloured powder or brittle solid with a characteristic odour. |
| Sodium content: |
Not less than 2.5% and not more than 5%. |
| Ester value: |
Not less than 90 and not more than 190 mg. KOH/g. |
| Total lactic acid (free and combined): |
Not less than 15% and not more than 40%. |
| Acid value: |
Not less than 60 and not more than 130 mg KOH/g. |
| E 482 Calcium stearoyl-2-lactylate. |
| Chemical description: |
A mixture of calcium salts of stearoyl lactylic acids with minor amounts of calcium salts of other related acids manufactured by the reaction of stearic acid and lactic acid. Other food fatty acids may also be present, free or esterified, due to their presence in the stearic acid used. |
| Description: |
White or slightly yellowish powder or brittle solid with a characteristic odour. |
| Calcium content: |
Not less than 1.0% and not more than 5.2%. |
| Ester value: |
Not less than 125 and not more than 190 mg KOH/g. |
| Total lactic acid: (free and combined). |
Not less than 15% and not more than 40%. |
| Acid value: |
Not less than 50 and not more than 130 mg KOH/g. |
| E 483 Stearyl tartrate. |
|
| Chemical description: |
Produced by the esterification of tartaric acid (E 334) with stearyl alcohol, consisting chiefly of the di-ester with minor amounts of mono-ester, tartaric acid and free stearyl alcohol. Other esters may also be present due to the presence in the stearyl alcohol used of alcohols derived from food fatty acids other than stearic acid. |
| Description: |
A cream coloured unctous solid at 25°C. |
| Total ester content: |
Not less than 90%. |
| Total tartaric acid content: |
Not less than 18% and not more than 35%. |
| Unsaponifiable matter: |
Not less than 77% and not more than 83% |
| Melting range: |
67°C-77°C. |
| Ester value: |
Not less than 163 and not more than 180. |
| Iodine value: |
Not more than 4 (Wijs). |
| Acid value: |
Not more than 6 mg KOH/g. |
| Sulphated ash: |
Not more than 0.5% determined at 800 ± 25°C. |
|
|
|
Polyoxyethylene (8) stearate.
|
|
|
The criteria in the monograph for polyoxyethylene (8) stearate contained in the Nutrition Meetings Report Series No. 35 (1964) of the United Nations' Food and Agriculture Organisation at page 118.
|
|
|
Polyoxyethylene (40) stearate.
|
|
|
The criteria in the monograph for polyoxyethylene (40) stearate contained in the Nutrition Meetings Report Series No. 35 (1964) of the United Nations' Food and Agriculture Organisation at page 127.
|
|
|
Polyoxyethylene (20) sorbitan monostearate or polysorbate 60.
|
|
|
The criteria in the monograph for polysorbate 60 contained in the Food Chemicals Codex 1972 at page 634 except that the final sentence of the description shall be deleted.
|
|
|
Polyoxyethylene (20) sorbitan tristearate or polysorbate 65.
|
|
|
The criteria in the monograph for polysorbate 65 contained in the Food Chemicals Codex 1972 at page 635 except that the final sentence of the description shall be deleted.
|
|
|
Polyoxyethylene (20) sorbitan monopalmitate or polysorbate 40.
|
|
|
The criteria in the monograph for polyoxyethylene (20) sorbitan monopalmitate contained in the Nutrition Meetings Report Series No. 35 (1964) of the United Nations' Food and Agriculture Organisation at page 135.
|
|
|
Polyoxyethylene (20) sorbitan monolaurate or polysorbate 20.
|
|
|
The criteria in the monograph for polysorbate 20 contained in the Food Chemicals Codex 1972 at page 632 as amended by the Second Supplement, 1975 at page 30.
|
|
|
Polyoxyethylene (20) sorbitan mono-oleate or polysorbate 80.
|
|
|
The criteria in the monograph for polysorbate 80 contained in the Food Chemicals Codex 1972 at page 637 as amended by the Second Supplement 1975 at page 30 except that the final sentence off the description shall be deleted.
|
|
|
Sorbitan monostearate.
|
|
|
The criteria in the monograph for sorbitan monostearate contained in the Food Chemicals Codex 1972 at page 784 except that the final sentence off the description shall be deleted.
|
|
|
Sorbitan tristearate.
|
|
|
The criteria in the monograph for sorbitan tristearate contained in the Nutrition Meetings Report Series No. 35 (1964) of the United Nations' Food and Agriculture Organisation at page 108.
|
|
|
Sorbitan monopalmitate.
|
|
|
The criteria in the monograph for sorbitan monopalmitate contained in the Nutrition Meetings Report Series No. 35 (1964) of the United Nations' Food and Agriculture Organisation at page 102.
|
|
|
Sorbitan monolaurate.
|
|
|
The criteria in the monograph for sorbitan monolaurate contained in the British Pharmaceutical Codex 1973 at page 465.
|
|
|
Sorbitan mono-oleate.
|
|
|
The criteria in the monograph for sorbitan mono-oleate contained in the British Pharmaceutical Codex 1973 at page 466.
|
|
|
Dioctyl sodium sulphosuccinate.
|
|
|
The criteria in the monograph for dioctyl sodium sulphosuccinate contained in the Food Chemicals Codex 1972 at page 256 as amended by the First Supplement, 1974 at page 16 except that the requirement for residue on ignition shall be calculated on a dry matter basis and that for the method of assay there shall be substituted the method of V.W Reid, G.F. Longman and E. Heinerth contained in Tenside, Zeitschrift for Physik, Chemic and Anwerdung Grenzflachenaktiver Stoffe, published by Carl Hanser, Munich, Federal Republic of Germany, 1967, volume 4, part 9 at page 302.
|
|
|
PART III.
|
|
|
General purity criteria applicable to permitted emulsifiers and permitted stabilisers except where otherwise provided by specific purity criteria.
|
|
|
Each emulsifier and stabiliser shall not contain--
|
|
|
(a) A toxicologically dangerous amount of any element, in particular heavy metals:
|
|
|
(b) more than 3 milligrams per kilogram al arsenic;
|
|
|
(c) more than 10 milligrams per kilogram of lead;
|
|
|
(d) more than 50 milligrams per kilogram of copper, or 25 milligrams per kilogram of zinc, or 50 milligrams per kilogram of any combination of copper and zinc.
|
|
|
SCHEDULE 2.
|
|
|
PART I.
|
|
|
Emulsifiers and Stabilisers permitted only in certain food.
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Column 1 |
Column 2 |
Column 3 |
| Specified food |
Permitted emulsifier or permitted stabiliser |
Milligrams per kilogram not exceeding-- |
|
(a) Dutch type rusks
|
Sodium, potassium and calcium salts of fatty acids |
15,000 (calculated as sodium oleate C18H33NaO2, and on the weight of the flour) |
|
(b) The permitted emulsifiers or permitted stabilisers:--
|
|
|
|
Mono-and di-glycerides of fatty acids; lactic acid esters of mono-and di- glycerides of fatty acids; sucrose esters of fatty acids; sucroglycerides polyglycerol esters of fatty acids; propane-1,2-diol esters of fatty acids
|
Sodium, potassium and calcium salts of fatty acids. |
60,000 (calculated as sodium oleate C18H33NaO2) |
|
(c) tin-greasing emulsions
|
Oxidatively polymerised soya bean oil |
In accordance with good manufacturing practice |
|
|
Polyglycerol esters of dimerised fatty acids of soya bean oil |
|
|
|
PART II.
|
|
|
Foods in which the use of Permitted Emulsifiers and Permitted Stabilisers is limited.
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Column 1 |
Column 2 |
Column 3 |
| Specified food |
Permitted emulsifier or permitted stabiliser |
Milligrams per kilogram not exceeding-- |
|
(a) Bread
|
Lecithins |
|
|
|
Mono-and di-glycerides of fatty acids |
|
|
|
Lactic acid esters of mono- and di-glycerides of fatty acids |
|
|
|
Citric acid esters of mono- and di-glycerides of fatty acids |
In accordance with good manufacturing practice |
|
|
Mono- and diacetyltartaric acid esters of mono- and di-glycerides of fatty acids |
|
|
|
Stearyl tartrate |
|
|
|
Sodium stearoyl 2-lactylate |
|
|
|
Calcium stearoyl-2-lactylate |
5,000 |
|
(b) Soft cheese, whey cheese, processed cheese, cheese spread
|
Lecithins
|
|
|
Alginic acid
|
|
|
Sodium alginate
|
|
| Calcium alginate |
|
| Carrageenan |
|
| Locust bean gum |
|
|
|
Tragacanth
|
In accordance with good manufacturing practice |
|
|
Acacia
|
|
|
|
Ghatti gum
|
|
|
|
Karaya gum or Sterculia gum
|
|
|
|
Xanthan gum
|
|
|
|
Guar gum |
|
|
|
Sodium orthophosphates
|
|
|
|
Sodium & Potassium polyphosphates (E 450). |
In accordance with good manufacturing practice |
|
(c) Cream which contains not less than 35 per cent milk-fat and which is sold as whipping cream or whipped cream
|
Alginic acid
|
|
|
Sodium alginate
|
|
| tetraSodium-diphosphate or tetra- Sodiumpyrophosphate |
|
|
Sodium carboxy-methlcellulose
|
|
| Carrageenan |
3,000 singly or in combination |
|
|
|
Footnote: The permitted emulsifiers or permitted stabilisers mono- and di-glycerides of fatty acids, lactic acid esters of mono- and di-glycerides of fatty acids, citric acid esters of mono- and di-glycerides of fatty acids and mono- and di-acetyltartaric acid esters of mono- and di-glycerides of fatty acids shall, when used in bread, have a hydroxyl value of the free combined fatty acids not exceeding 2.
|
|
|
SCHEDULE 3.
|
|
|
Labelling of Permitted Emulsifiers and Permitted Stabilisers.
|
|
|
1. (1) Each container to which article 9 (1) relates shall bear a label on which is printed a true statement:--
|
|
|
( a ) In respect of each permitted emulsifier or permitted stabiliser present, of the serial number, if any, as specified in relation thereto in column 2 of Part I of Schedule 1, and of the common or usual name or an appropriate designation of that permitted emulsifier or permitted stabiliser;
|
|
|
( b ) where any other substance or substances is or are present:--
|
|
|
(i) of the common or usual name or an appropriate designation of each such substance;
|
|
|
(ii) of the proportion of each such substance in respect of which any Regulations, other than these Regulations, made under the Act contain a requirement to that effect; and
|
|
|
( c ) in the case of emulsifiers to which sugars have been added, the statement "standardised with sugar" shall be added to the designation on the label.
|
|
|
(2) The said statement shall be headed or preceded by the words "for foodstuffs (restricted use)".
|
|
|
(3) The container shall have on it the name and address of the person importing or the person selling the substance in the container or, if the substance is manufactured within the State, the name of the manufacturer of the substance.
|
|
|
2. Any statement required by the preceding paragraph:--
|
|
|
( a ) shall be clear and legible;
|
|
|
( b ) shall be in a conspicuous position on the label which shall be marked on, or securely attached to, the container in such a manner that it will be readily discernible and easily read by an intending purchaser under normal conditions of purchase;
|
|
|
( c ) shall not be in any way hidden or obscured or reduced in conspicuousness by any other matter, whether pictorial or not, appearing on the label.
|
|
|
3. The figures and letters in every word in any statement to which the preceding paragraph applies:--
|
|
|
( a ) shall be in characters of uniform colour and size (being not less than 1.5 millimetres in height for a label on a container of which the greatest dimension does not exceed 12 centimetres and not less than 3 millimetres in height for a label on a container of which the greatest dimension exceeds 12 centimetres), but so that the initial letter of any word may be taller than any other letter in the word;
|
|
|
( b ) shall appear on a contrasting ground, so however that where there is no ground other than such as is provided by a transparent container and the contents of that container are visible behind the letters, those contents shall be taken to be the ground for the purposes of this paragraph;
|
|
|
( c ) shall be within a surrounding line and no other written or pictorial matter shall appear within that line.
|
|
|
4. For the purposes of this Schedule--
|
|
|
( a ) the height of any lower case letter shall be taken to be the height thereof, disregarding any ascender or descender thereof;
|
|
|
( b ) any requirement that figures or letters shall be of uniform height, colour or size, shall be construed as being subject to the saving that any inconsiderable variation in height, colour or size, as the case may be, may be disregarded.
|
|
|
GIVEN under the Official Seal of the Minister for Health this 8th day of February 1980.
|
|
|
MICHAEL WOODS,
|
|
|
Minister for Health.
|
|
|
EXPLANATORY NOTE.
|
|
|
The regulations prohibit the manufacture, importation, distribution or sale of food which contains any emulsifier or stabiliser other than a permitted emulsifier or stabiliser and prescribe criteria of purity for these substances. In addition, the regulations specify that certain emulsifiers and stabilisers may be used only in particular foodstuffs and restrict other specified foods to containing only particular permitted emulsifiers and stabilisers, subject to prescribed limits in each case.
|
|
|
The regulations prohibit the manufacture, importation, distribution, sale or advertisement for sale of any emulsifier or stabiliser for use as an ingredient in the preparation of food, other than a permitted emulsifier or stabiliser. Also, the regulations prescribe labelling requirements for permitted emulsifiers and stabilisers to be sold as ingredients in the preparation of food and prohibit the labelling or advertising of any permitted emulsifier or stabiliser to be sold as an ingredient in the preparation of food which would indicate that the substance is a nutritive substitute for fat or eggs.
|
|
|
The regulations provide that where a sample of food has been certified not to comply with the regulations an authorised officer may seize, remove and detain such food as being food which is unfit for human consumption and, in certain circumstances, destroy it.
|
|
|
The regulations implement Directives No. 74/329/EEC (O.J. No. L189, 12/7/1974, P.1.) 78/612/EEC (O.J. No. L197, 22/7/78, P22) and 78/663/EEC (O.J. No. L223, 14/8/78, P.7) of the European Economic Communities relating to emulsifiers, stabilisers, thickening and gelling agents authorised for use in foodstuffs intended for human consumption.
|
|
|
The Health (Arsenic and Lead in Food) Regulations, 1972 and the Health (Antioxidant in Food) Regulations, 1973 will be amended in consequence of the regulations and the provision of the Public Health (Saorstát Éireann) (Preservatives etc. in Food), Regulations, 1928, which prohibits the presence of thickening substances in cream will be repealed.
|
|
|
|